Last Updated on 16/07/2024 by yojanaparichay.com
Mid Day Meal Scheme : Millions of children’s general well-being, school enrollment, and malnutrition have all been improved by the Mid Day Meal Scheme, a mainstay of India’s social welfare and education systems. This article explores the scheme’s complexities, development, effects, difficulties, and future directions.
What is Mid Day Meal Scheme ?
The Mid Day Meal Scheme was started in 1995.The Mid Day Meal SchemeScheme is a government-run program in India that provides free cooked meals to children in government and government-aided primary schools. Its primary goal is to improve the nutritional status of children and boost school attendance, especially among disadvantaged groups. By offering a hot, cooked meal, the scheme aims to address hunger, malnutrition, and encourage children to attend school regularly.
Evolution of the Mid-Day Meal Scheme
- The Mid Day Meal Scheme has its origins in a comparable program that Madras Municipal Corporation started in the early 1900s. However, the concept became well-known across the country in the middle of the 1990s.
- The Mid-Day Meal Scheme was modeled after the National Programme of Nutritional Support to Primary Education (NP-NSPE), which was introduced in 1995. It sought to raise school attendance and improve nutritional status.
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme (MDMS): All government and government-aided elementary schools were required to implement the Mid-Day Meal Scheme in 2001 by the Supreme Court. This signified a major program expansion.
- PM Poshan Shakti Nirman: In 2021, the initiative changed its name to PM Poshan Shakti Nirman, reiterating its emphasis on child nutrition and fortifying it.

Goals of the Mid Day Meal Scheme
One of the main pillars of India’s social welfare and education systems is the Mid-Day Meal Scheme, which has the following main goals:
- Enhancing Nutritional Status: Serving hot meals to kids while they’re at school can combat malnutrition and enhance their general health and wellbeing.
- Improving School Enrollment: Offering a free breakfast to parents encourages them to bring their kids to school, which raises enrollment rates, particularly in underprivileged areas.
- Increasing School Attendance: Providing a daily lunch encourages students to attend class regularly, which lowers absenteeism and dropout rates.
- Reducing Dropout Rates: The program strives to keep kids in school until they have completed their basic education by tackling hunger and offering a supportive school environment.
- Addressing Social Inequalities: Reaching out to children from disadvantaged backgrounds, including those belonging to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, to ensure equitable access to education and nutrition.
- Supporting Local Economy: Generating employment opportunities for women and other marginalized groups involved in food production, processing, and distribution.
- Promoting Gender Equality: Encouraging equal access to education for girls by providing them with a nutritious meal.
Implementation of the Mid-Day Meal Scheme
The Mid Day Meal Scheme is implemented through a decentralized model involving the central government, state governments, and local bodies. Key aspects of implementation include:
- Menu Planning: A nutritionally balanced menu is prepared, adhering to dietary guidelines and local food preferences.
- Food Procurement: Local procurement of food grains and other ingredients is prioritized to support local farmers and economies.
- Cooking and Distribution: Meals are cooked and served in schools, often with the involvement of local women’s self-help groups.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation are conducted to assess the scheme’s effectiveness and address any shortcomings.

Impact of the Mid-Day Meal Scheme
The Mid Day Meal Scheme has had a profound impact on the lives of millions of children in India. Some of the key outcomes include:
- Improved Nutritional Status: A significant reduction in malnutrition and anemia among school-aged children.
- Increased School Enrollment: A rise in school enrollment rates, particularly among girls and children from marginalized communities.
- Enhanced Learning Outcomes: Better attendance and concentration in class due to improved nutrition and reduced hunger.
- Empowerment of Women: Generation of employment opportunities for women involved in meal preparation and distribution.
- Economic Impact: Boost to local economies through the procurement of food grains and other ingredients.
Eligibility criteria
- Students in government and government-aided schools: Students studying in government and government-aided schools throughout India are the main focus of this programme. Children who are enrolled in primary through secondary education programs are eligible to receive benefits from the program.
- Age requirements: Children between the ages of 6 and 14 are normally covered by the program. However, particular age restrictions could range slightly between states or based on regional differences in educational programs.
- Socioeconomic criteria: Children from low-income families are the target audience for the Mid Day Meals Scheme. Children from underprivileged areas or households with below-the-poverty-line (BPL) status are typically given preference when it comes to program enrollment.
- Attendance at school: Attending school regularly is one of the program’s primary qualifying requirements. For students to be eligible for midday meals, frequent attendance at school is required.
- Enrolled in approved schools: In order for children to be eligible for the program, they must be enrolled in schools that have been approved by the relevant education authorities. The program is mostly run in schools that follow the directives and criteria set forth by the government for education.

Procedure for Applications
Step 1: Make an appointment with the school
- The Mid Day Meal Scheme requires parents or guardians of eligible pupils to visit the specific school where they would want to enroll their child. They will have to complete the registration form that the administration of the institution will supply.
Step 2: Eligibility Verification
- The student’s eligibility will be confirmed by the school administration based on factors including age, attendance at an accredited institution, and socioeconomic status. If required, they could ask for pertinent papers or hold interviews.
Step 3: Verification of Enrollment
- The school administration will inform parents or guardians that their kid has successfully enrolled in the Mid Day Meal Scheme when eligibility has been verified. They will include information on when the meals will start as well as any further instructions.
Step 4: Consistent Attendance
- In order to retain eligibility for the program, the student has to continue attending classes on a regular basis. The school administration will keep an eye on the attendance records to make sure the students are actively participating in the program.
Step 5: Distribution of Meals
- The enrolled pupils will get the allocated midday meals during school hours. Depending on the school’s facilities, meals are typically provided on campus, either in the classrooms or in a special eating hall.
Step 6: Ongoing Assessment
- Periodic assessments of the Mid Day Meals Scheme’s impact and efficacy may be carried out by the school administration. In order to make the required adjustments, this review may entail gathering input from parents, instructors, and students.
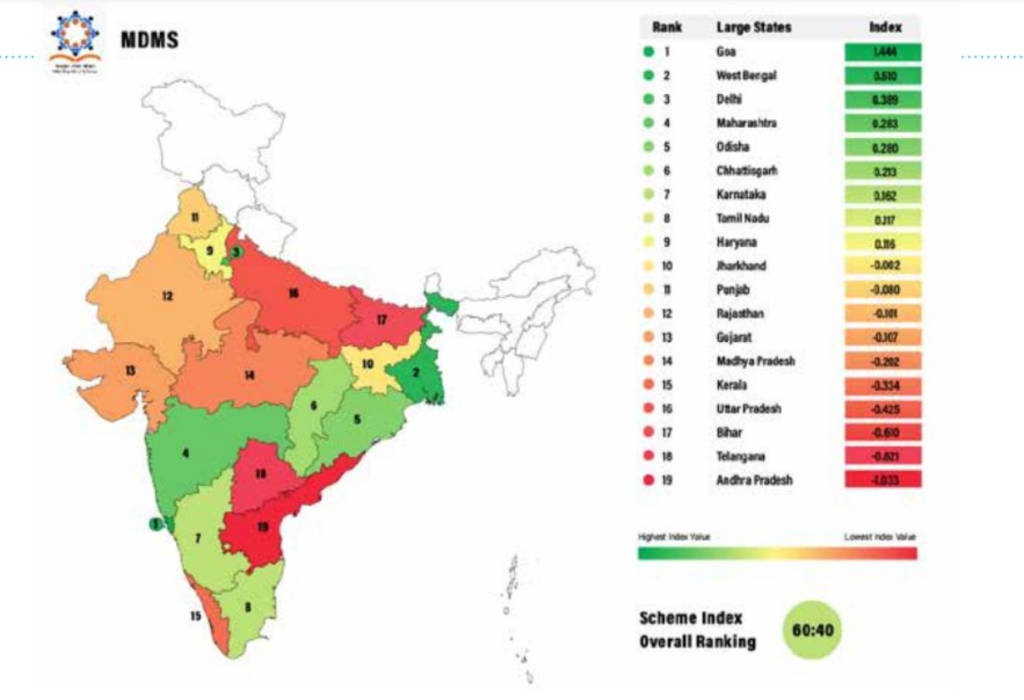
Conclusion
The Mid Day Meal Scheme stands as a testament to India’s commitment to child nutrition, education, and social welfare. It has emerged as one of the world’s largest school feeding programs, impacting the lives of millions. By addressing the challenges and building upon its strengths, the scheme can continue to be a powerful tool for achieving India’s development goals.
Friends, how did you like the information given about Mid Day Meal Scheme? You can tell us by commenting. If you have any suggestion regarding the article, then you can tell us by commenting. Friends, keep visiting our website https://yojanaparichay.com/ to get updated information related to such government schemes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) :
Who is eligible for the Mid Day Meal Scheme?
Children studying in government, government-aided, and local body schools, as well as EGS and AIE centers, are eligible.
How is the food prepared and distributed?
Meals are typically cooked at the school premises, often with the involvement of local women’s self-help groups.
What is the role of the state government in the scheme?
State governments are responsible for the implementation of the scheme within their respective states, including monitoring and evaluation.i
What kind of food is provided?
A hot cooked meal, typically vegetarian, is provided. The menu varies based on local availability and nutritional guidelines.
Are there nutritional standards for the meals?
Yes, there are prescribed nutritional standards for the meals, specifying calorie and protein content.
How is food safety ensured?
There are guidelines for food hygiene and safety, including regular inspections and training for cooks.
Is there a cost for the meal?
No, the meals are provided free of cost to students.
Who bears the cost of the Mid Day Meal Scheme?
The program is funded in part by the central government and the states.
How is the scheme funded?
The scheme is funded through budgetary allocations from the central and state governments.

